AIM
4/20/23
5
−
4
−
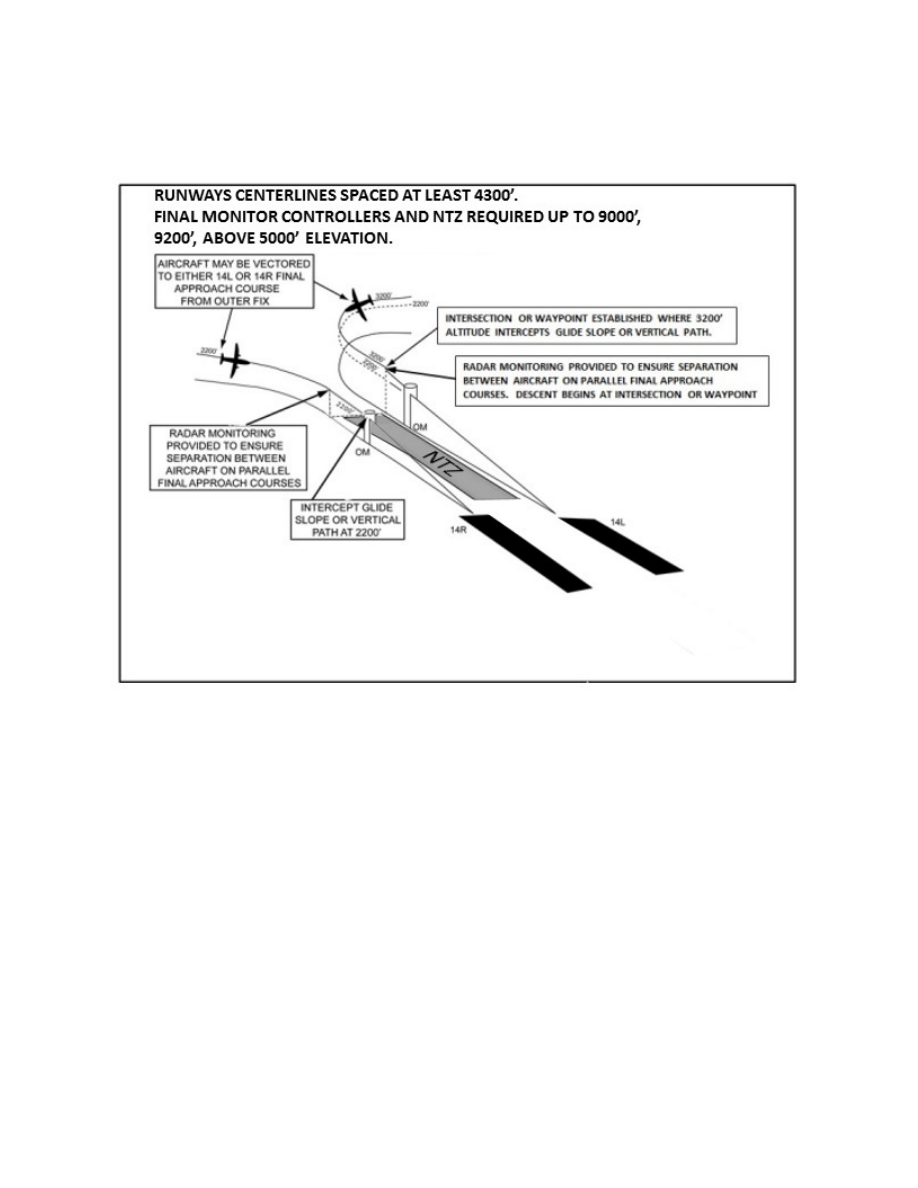
15. Simultaneous Independent ILS/RNAV/GLS Approaches
FIG 5
−
4
−
22
Simultaneous Independent ILS/RNAV/GLS Approaches
a. System.
An approach system permitting simultaneous approaches to parallel runways with centerlines
separated by at least 4,300 feet. Separation between 4,300 and 9,000 feet (9,200’ for airports above 5,000’)
utilizing NTZ final monitor controllers. Simultaneous independent approaches require NTZ radar monitoring
to ensure separation between aircraft on the adjacent parallel approach course. Aircraft position is tracked by
final monitor controllers who will issue instructions to aircraft observed deviating from the assigned final
approach course. Staggered radar separation procedures are not utilized. Integral parts of a total system are radar,
communications, ATC procedures, and ILS or other required airborne equipment. A chart note identifies that the
approach is authorized for simultaneous use.
When simultaneous operations are in use, it will be advertised on the ATIS. When advised that simultaneous
approaches are in use, pilots must advise approach control immediately of malfunctioning or inoperative
receivers, or if a simultaneous approach is not desired. Although non
−
precision minimums may be published,
pilots must only use those procedures specifically authorized by chart note. For example, the chart note “LNAV
NA during simultaneous operations,” requires vertical guidance. When given a choice, pilots should always fly
a precision approach whenever possible.
NOTE
−
ATC does not use the word independent or parallel when advertising these operations on the ATIS.
EXAMPLE
−
Simultaneous ILS Runway 24 left and ILS Runway 24 right approaches in use.
b.
Radar Services. These services are provided for each simultaneous independent approach.
Arrival Procedures
5
−
4
−
44