AIM
4/20/23
(2)
If shutdown on a helideck, request the supervisor in charge provide a briefing on location of
protective equipment and safety procedures.
(3)
If while flying near a helideck and the visual red beacon alarm is observed or an unusually strong
odor of “rotten eggs” is detected, immediately don the protective air pack, exit to an area upwind, and notify the
suspected source field of the hazard.
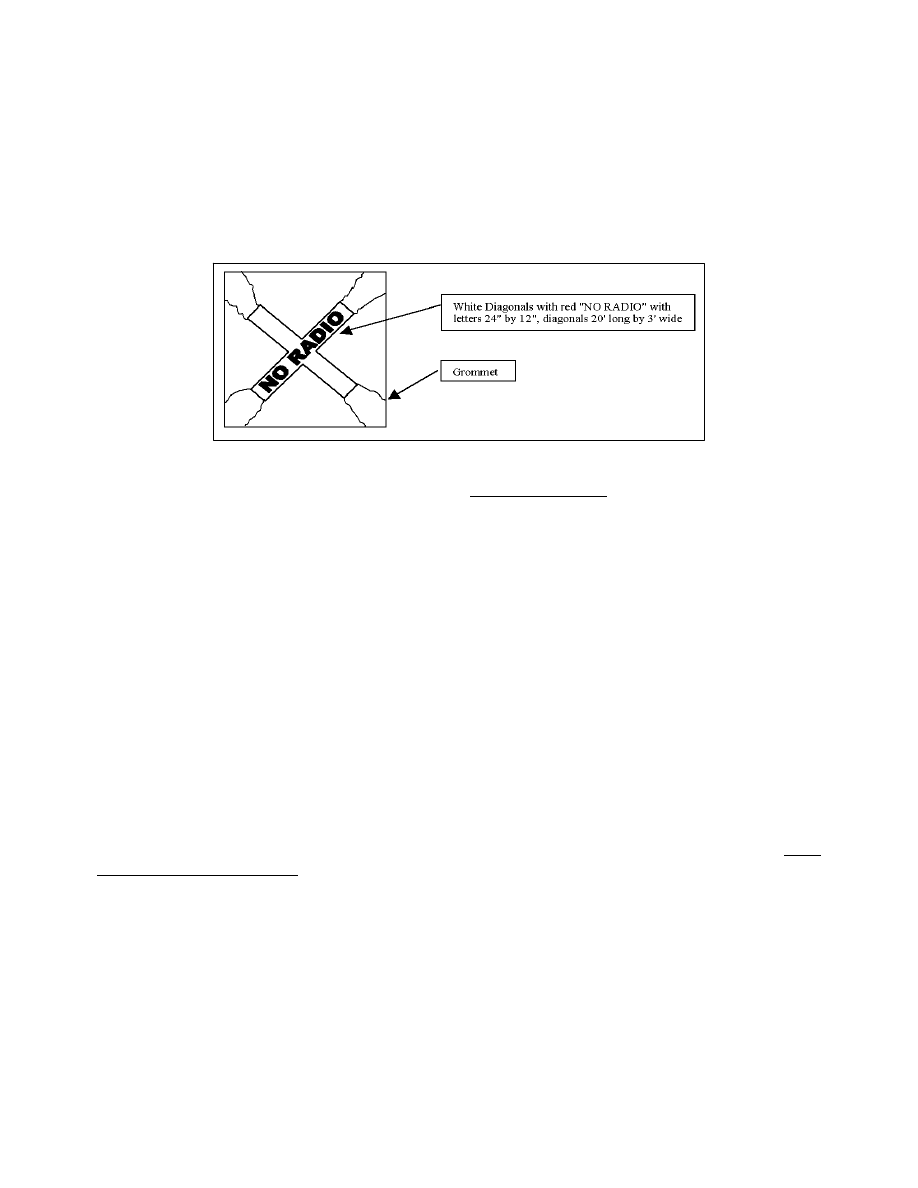
FIG 10
−
2
−
1
Closed Helideck Marking
−
No Radio
(b) Oil Field Supervisors
(1)
If presence of hydrogen sulfide is detected, a red rotating beacon or red high intensity strobe light
adjacent to the primary helideck stairwell or wind indicator on the structure should be turned on to provide visual
warning of hazard. If the beacon is to be located near the stairwell, the State of Louisiana “Offshore Heliport
Design Guide” and FAA Advisory Circular (AC) 150/5390
−
2A, Heliport Design Guide, should be reviewed to
ensure proper clearance on the helideck.
(2)
Notify nearby helicopter operators and bases of the hazard and advise when hazard is cleared.
(3)
Provide a safety briefing to include location of protective equipment to all arriving personnel.
(4)
Wind socks or indicator should be clearly visible to provide upwind indication for the pilot.
h. Gas Venting Helideck/Heliport Operational Hazard Warning(s)/Procedures
−
Operations Near Gas
Vent Booms
1. Background.
Ignited flare booms can release a large volume of natural gas and create a hot fire and
intense heat with little time for the pilot to react. Likewise, unignited gas vents can release reasonably large
volumes of methane gas under certain conditions. Thus, operations conducted very near unignited gas vents
require precautions to prevent inadvertent ingestion of combustible gases by the helicopter engine(s). The
following practices are recommended.
2. Pilots
(a)
Gas will drift upwards and downwind of the vent. Plan the approach and takeoff to observe and avoid
the area downwind of the vent, remaining as far away as practicable from the open end of the vent boom.
(b)
Do not attempt to start or land on an offshore helideck when the deck is downwind of a gas vent unless
properly trained personnel verify conditions are safe.
3. Oil Field Supervisors
(a)
During venting of large amounts of unignited raw gas, a red rotating beacon or red high intensity
strobe light adjacent to the primary helideck stairwell or wind indicator should be turned on to provide visible
warning of hazard. If the beacon is to be located near the stairwell, the State of Louisiana “Offshore Heliport
Design Guide” and FAA AC 150/5390
−
2A, Heliport Design Guide, should be reviewed to ensure proper
clearance from the helideck.
(b)
Notify nearby helicopter operators and bases of the hazard for planned operations.
10
−
2
−
4
Special Operations