AIM
4/20/23
(e) Voice Communication Capabilities (Item 10a)
The FAA does not require indication of voice communication capabilities in a flight plan for domestic flights,
but it is permissible. For flights outside the domestic United States, all relevant capabilities must be indicated
as follows (See TBL 4
−
11):
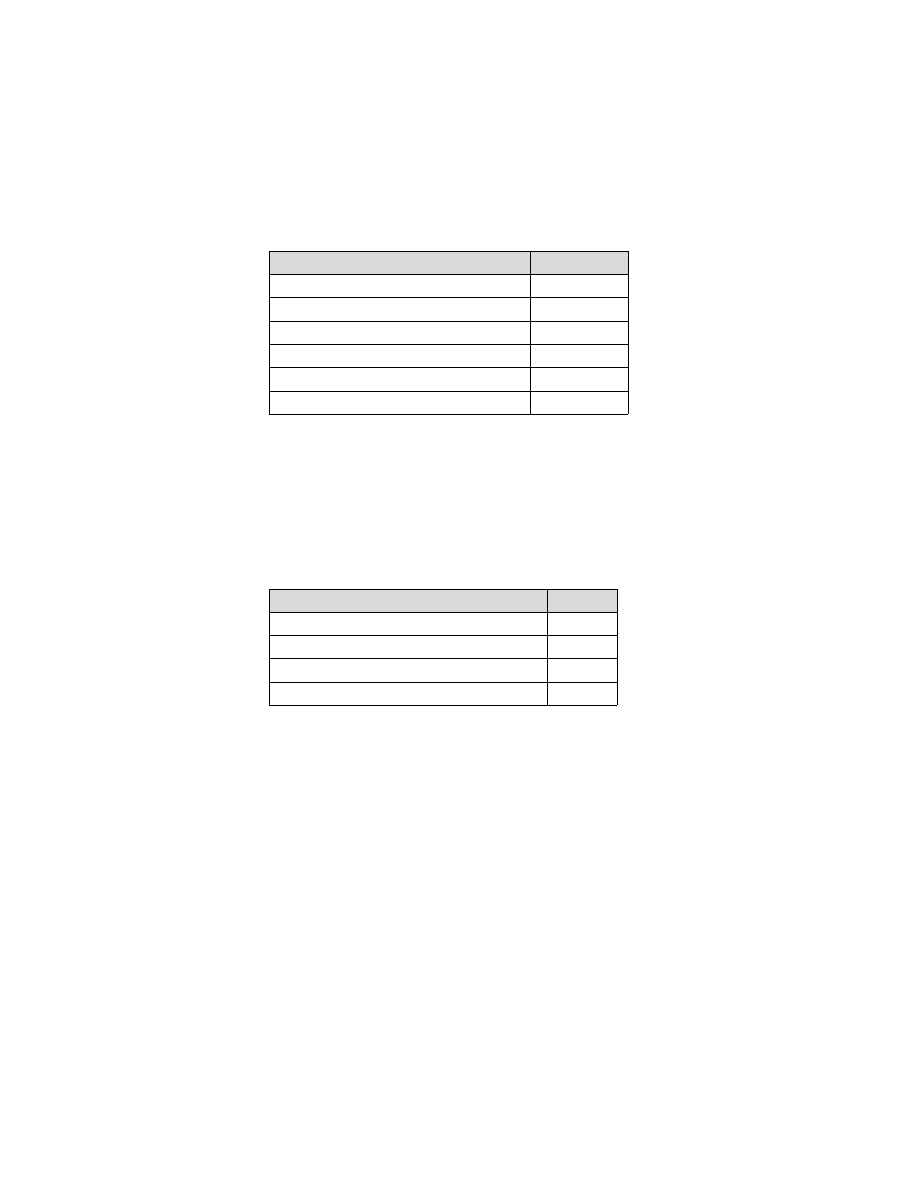
TBL 4
−
11
Voice Communication Capabilities
Capability
Item 10a
VHF Radio
V
UHF Radio
U
HF Radio
H
VHF Radio (8.33 kHZ Spacing)
Y
ATC SATVOICE (INMARSAT)
M1
ATC SATVOICE (Iridium)
M3
(f)
Approach Aid Capabilities (Item 10a).
The FAA does not require filing of approach aid capability in order to request a specific type of approach,
however any of the codes indicated in TBL 4
−
12 in 10a are permissible.
International flights may be required to indicate approach capability, based on instructions from
relevant service providers.
TBL 4
−
12
Approach Aid Capabilities
Capability
Item 10a
ILS
L
MLS
K
LPV Approach (APV with SBAS) (WAAS)
B
GBAS Landing System (LAAS)
A
6.
Performance
−
Based Navigation Routes (Item 10a, Item 18 PBN/, Item 18 NAV/)
−
When planning to fly
routes that require PBN capability, file the appropriate capability as shown in TBL 4
−
13.
Appendix 4
−
10
FAA Form 7233
−
4
−
International Flight Plan