4/20/23
AIM
There is no U.S. requirement to file the aircraft Mode S Code in Item 18.
6. SELCAL code (Item 18 SEL/)
(a)
Flights with HF radio and Selective Calling capability should include their 4
−
letter SELCAL code. Per
the U.S. AIP, GEN 3.4, Paragraph 9, Selective Calling System (SELCAL) Facilities Available.
(b)
The SELCAL is a communication system that permits the selective calling of individual aircraft over
radio
−
telephone channels from the ground station to properly equipped aircraft, to eliminate the need for the
flight crew to constantly monitor the frequency in use.
EXAMPLE
−
SEL/CLEF
7. Performance Category (Item 18 PER/)
Include the appropriate single
−
letter Aircraft Approach Category as defined in the Pilot/Controller Glossary.
EXAMPLE
−
PER/A
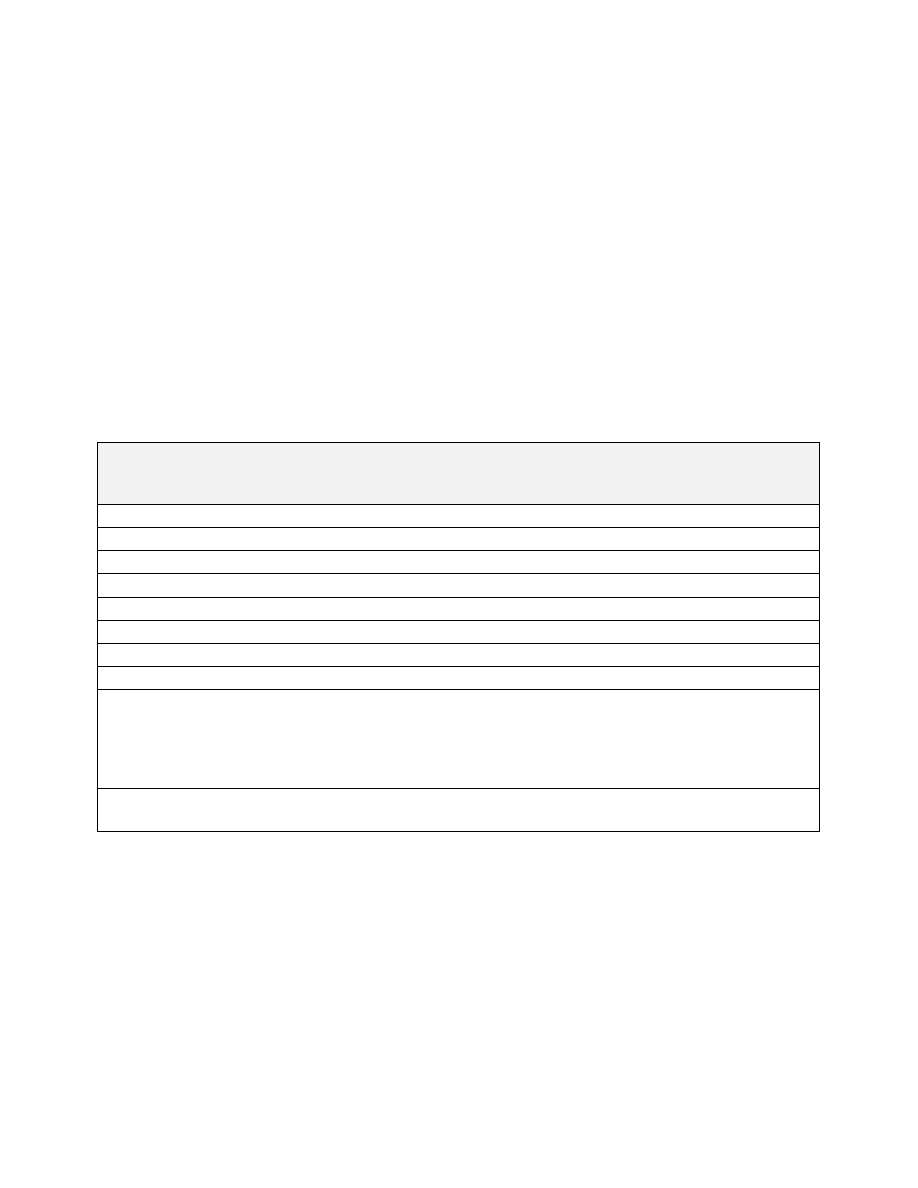
TBL 4
−
20
Flight Routing Information
Item
International Flight Plan
(FAA Form 7233
−
4)
Domestic U.S. Requirements
Equivalent Item on
Domestic Flight Plan
(FAA Form 7233
−
1)
Departure Airport
Item 13
Required
Item 2
Departure Time
Item 13
Required
Item 1
Cruise Speed
Item 15
Required
N/A
Requested Altitude
Item 15
Required
Item 3
Route
Item 15
Required
N/A
Delay En Route
Item 15, Item 18 DLE/
Required
N/A
Destination Airport
Item 16
Required
Item 11
Total Estimated Elapsed Time
Item 16
Required
Item
Alternate Airport
Item 16
Item 18 ALTN/ (Destination Alternate).
RALT/ (En route Alternate); TALT/
(Take
−
off Alternate)
If necessary
No need to file for domestic U.S. flight
N/A
Estimated Elapsed Times
Item 18 EET/
Include when filing flight plan with center
other than departure center
N/A
f. Instructions for Flight Routing Items
1. Departure Airport (Item 13, Item 18 DEP/)
(a)
Enter the departure airport. The airport should be identified using the four
−
letter location identifier from
FAA Order JO 7350.9, Location Identifiers, or from ICAO Document 7910. FSS and FAA contracted flight plan
filing services will allow up to 11 characters in the departure field. This will permit entry of non
−
ICAO identifier
airports, and other fixes such as an intersection, fix/radial/distance, and latitude/longitude coordinates. Other
electronic filing services may require a different format.
NOTE
−
While user interfaces for flight plan filing are not specified, all flight plan filing services must adhere to the appropri-
ate Interface Control Document upon transmission of the flight plan to the control facility.
(b)
When the intended departure airport (Item 13) is outside of domestic U.S. airspace, or if using the paper
version of FAA Form 7233
−
4, or DoD equivalent, if the chosen flight plan filing service does not allow
FAA Form 7233
−
4
−
International Flight Plan
Appendix 4
−
17