AIM
4/20/23
FIG 4
−
1
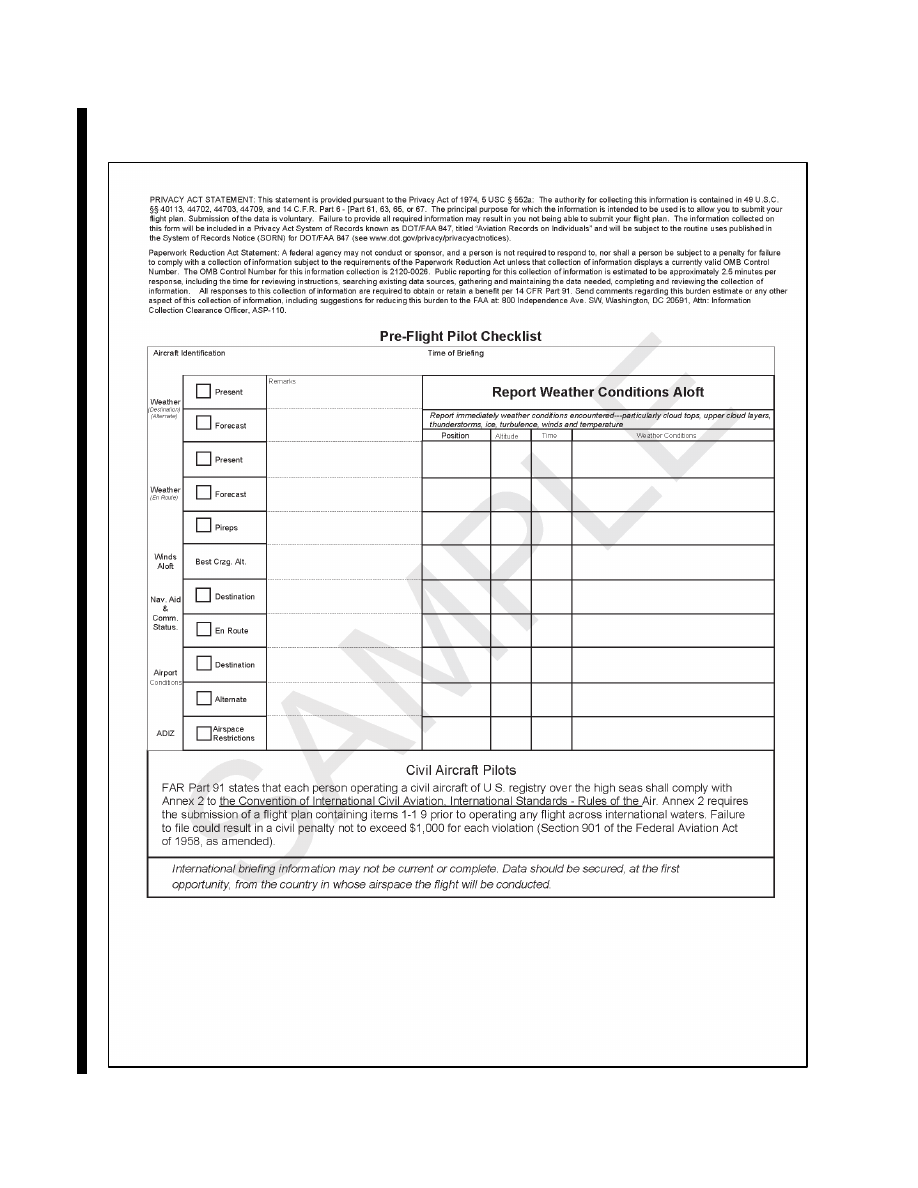
FAA Form 7233
−
4, Pre
−
Flight Pilot Checklist and International Flight Plan
Appendix 4
−
22
FAA Form 7233
−
4
−
International Flight Plan

AIM
4/20/23
FIG 4
−
1
FAA Form 7233
−
4, Pre
−
Flight Pilot Checklist and International Flight Plan
Appendix 4
−
22
FAA Form 7233
−
4
−
International Flight Plan