3/21/24
AIM
TBL 1
−
1
−
2
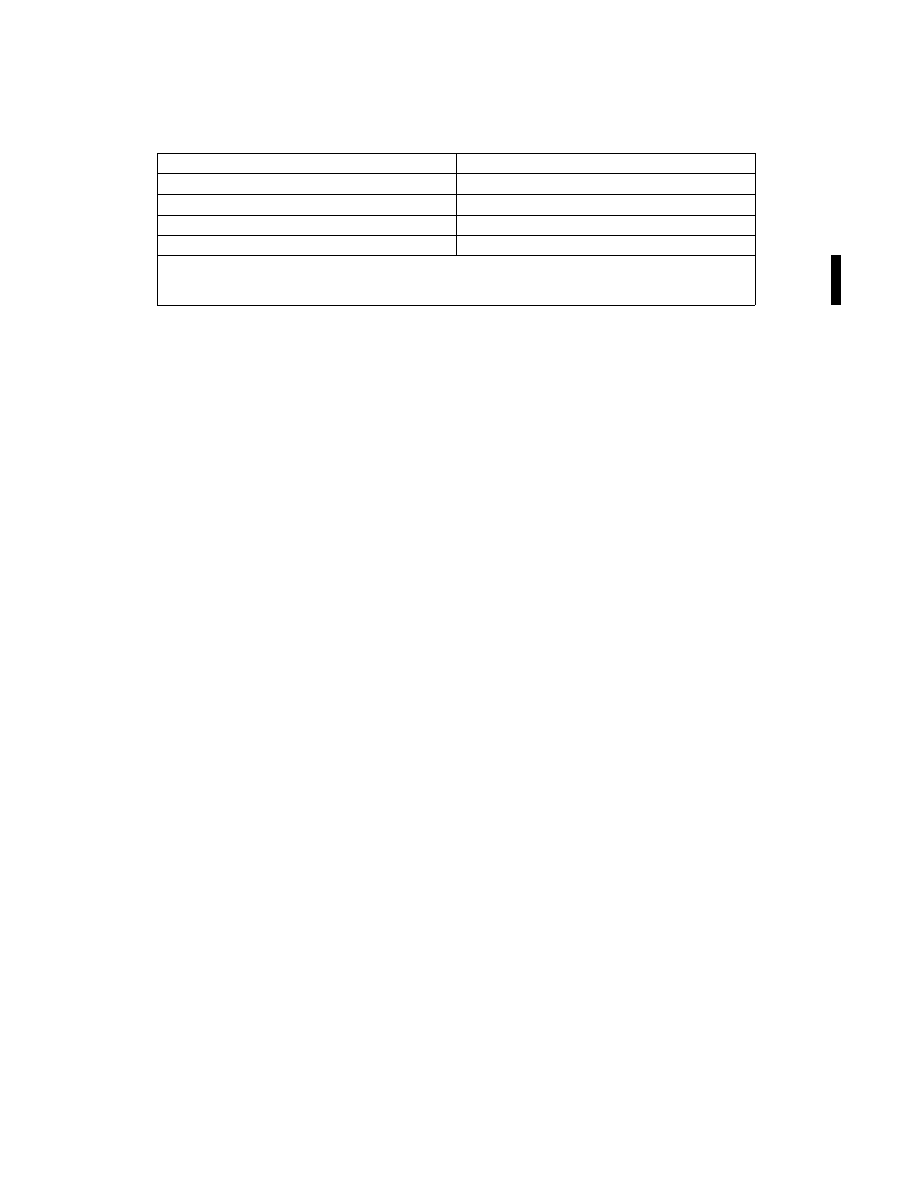
NDB Service Volumes
Class
Distance (Radius) (NM)
Compass Locator
15
MH
25
H
50*
HH
75
*Service ranges of individual facilities may be less than 50 nautical miles (NM). Restrictions to service
volumes are first published as a Notice to Air Missions and then with the alphabetical listing of the NAVAID
in the Chart Supplement.
1
−
1
−
9. Instrument Landing System (ILS)
a. General
1.
The ILS is designed to provide an approach path for exact alignment and descent of an aircraft on final
approach to a runway.
2.
The basic components of an ILS are the localizer, glide slope, and Outer Marker (OM) and, when installed
for use with Category II or Category III instrument approach procedures, an Inner Marker (IM).
3.
The system may be divided functionally into three parts:
(a) Guidance information:
localizer, glide slope.
(b) Range information:
marker beacon, DME.
(c) Visual information:
approach lights, touchdown and centerline lights, runway lights.
4.
The following means may be used to substitute for the OM:
(a)
Compass locator; or
(b)
Precision Approach Radar (PAR); or
(c)
Airport Surveillance Radar (ASR); or
(d)
Distance Measuring Equipment (DME), Very High Frequency Omni
−
directional Range (VOR), or
Nondirectional beacon fixes authorized in the Standard Instrument Approach Procedure; or
(e)
Very High Frequency Omni
−
directional Radio Range (VOR); or
(f)
Nondirectional beacon fixes authorized in the Standard Instrument Approach Procedure; or
(g)
A suitable RNAV system with Global Positioning System (GPS), capable of fix identification on a
Standard Instrument Approach Procedure.
5.
Where a complete ILS system is installed on each end of a runway; (i.e., the approach end of Runway
4 and the approach end of Runway 22) the ILS systems are not in service simultaneously.
b. Localizer
1.
The localizer transmitter operates on one of 40 ILS channels within the frequency range of 108.10 to
111.95 MHz. Signals provide the pilot with course guidance to the runway centerline.
2.
The approach course of the localizer is called the front course and is used with other functional parts, e.g.,
glide slope, marker beacons, etc. The localizer signal is transmitted at the far end of the runway. It is adjusted
for a course width of (full scale fly
−
left to a full scale fly
−
right) of 700 feet at the runway threshold.
3.
The course line along the extended centerline of a runway, in the opposite direction to the front course
is called the back course.
Navigation Aids
1
−
1
−
11