521
Federal Aviation Administration, DOT
§ 135.609
specified in this section, the FAA must
publish notice of change in the F
ED
-
ERAL
R
EGISTER
and the material must
be available to the public. All approved
material is available for inspection at
the FAA’s Office of Rulemaking (ARM–
1), 800 Independence Avenue SW., Wash-
ington, DC 20591 (telephone (202) 267–
9677) and from the sources indicated
below. It is also available for inspec-
tion at the National Archives and
Records Administration (NARA). For
information on the availability of this
material at NARA, call (202) 741–6030 or
go to
http://www.archives.gov/fed-
eral
_
register/code
_
of
_
federal
_
regulations/
ibr
_
locations.html.
(1) U.S. Department of Transpor-
tation, Subsequent Distribution Office,
DOT Warehouse M30, Ardmore East
Business Center, 3341 Q 75th Avenue,
Landover, MD 20785; telephone (301)
322–5377. Copies are also available on
the FAA’s Web site. Use the following
link and type the TSO number in the
search box:
http://rgl.faa.gov/Regu-
latory
_
and
_
Guidance
_
Library/rgTSO.nsf/
Frameset?OpenPage.
(i) TSO C–194, Helicopter Terrain
Awareness and Warning System
(HTAWS), Dec. 17, 2008.
(ii) [Reserved]
(2) RTCA, Inc., 1150 18th Street NW.,
Suite 910, Washington, DC 20036, tele-
phone (202) 833–9339, and are also avail-
able on RTCA’s Web site at
http://
www.rtca.org/onlinecart/index.cfm.
(i) RTCA DO–309, Minimum Oper-
ational Performance Standards
(MOPS) for Helicopter Terrain Aware-
ness and Warning System (HTAWS)
Airborne Equipment, Mar. 13, 2008.
(ii) [Reserved]
§ 135.607 Flight Data Monitoring Sys-
tem.
After April 23, 2018, no person may
operate a helicopter in air ambulance
operations unless it is equipped with an
approved flight data monitoring sys-
tem capable of recording flight per-
formance data. This system must:
(a) Receive electrical power from the
bus that provides the maximum reli-
ability for operation without jeopard-
izing service to essential or emergency
loads, and
(b) Be operated from the application
of electrical power before takeoff until
the removal of electrical power after
termination of flight.
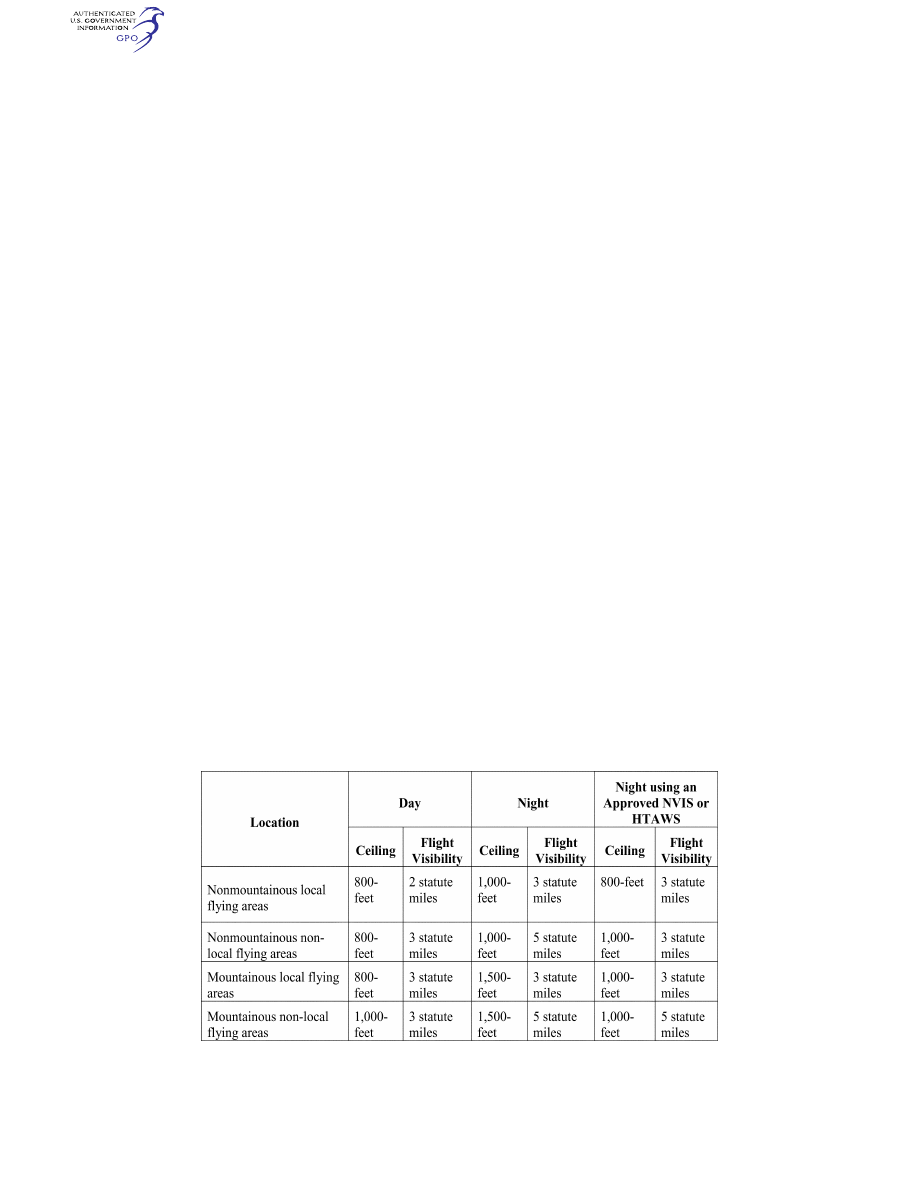
§ 135.609 VFR ceiling and visibility re-
quirements for Class G airspace.
(a) Unless otherwise specified in the
certificate holder’s operations speci-
fications, when conducting VFR heli-
copter air ambulance operations in
Class G airspace, the weather mini-
mums in the following table apply:

522
14 CFR Ch. I (1–1–24 Edition)
§ 135.611
(b) A certificate holder may des-
ignate local flying areas in a manner
acceptable to the Administrator, that
must—
(1) Not exceed 50 nautical miles in
any direction from each designated lo-
cation;
(2) Take into account obstacles and
terrain features that are easily identi-
fiable by the pilot in command and
from which the pilot in command may
visually determine a position; and
(3) Take into account the operating
environment and capabilities of the
certificate holder’s helicopters.
(c) A pilot must demonstrate a level
of familiarity with the local flying
area by passing an examination given
by the certificate holder within the 12
calendar months prior to using the
local flying area.
[Doc. No. FAA–2010–0982, 79 FR 9975, Feb. 21,
2014; Amdt. 135–129A, 79 FR 41126, July 15,
2014]
§ 135.611 IFR operations at locations
without weather reporting.
(a) If a certificate holder is author-
ized to conduct helicopter IFR oper-
ations, the Administrator may author-
ize the certificate holder to conduct
IFR helicopter air ambulance oper-
ations at airports with an instrument
approach procedure and at which a
weather report is not available from
the U.S. National Weather Service
(NWS), a source approved by the NWS,
or a source approved by the FAA, sub-
ject to the following limitations:
(1) The certificate holder must obtain
a weather report from a weather re-
porting facility operated by the NWS, a
source approved by the NWS, or a
source approved by the FAA, that is lo-
cated within 15 nautical miles of the
airport. If a weather report is not
available, the certificate holder may
obtain weather reports, forecasts, or
any combination of them from the
NWS, a source approved by the NWS,
or a source approved by the FAA, for
information regarding the weather ob-
served in the vicinity of the airport;
(2) Flight planning for IFR flights
conducted under this paragraph must
include selection of an alternate air-
port that meets the requirements of
§§ 135.221 and 135.223;
(3) In Class G airspace, IFR depar-
tures with visual transitions are au-
thorized only after the pilot in com-
mand determines that the weather con-
ditions at the departure point are at or
above takeoff minimums depicted in a
published departure procedure or VFR
minimum ceilings and visibilities in
accordance with § 135.609.
(4) All approaches must be conducted
at Category A approach speeds as es-
tablished in part 97 or those required
for the type of approach being used.
(b) Each helicopter air ambulance op-
erated under this section must be
equipped with functioning severe
weather detection equipment, unless
the pilot in command reasonably deter-
mines severe weather will not be en-
countered at the destination, the alter-
nate destination, or along the route of
flight.
(c) Pilots conducting operations pur-
suant to this section may use the
weather information obtained in para-
graph (a) to satisfy the weather report
and forecast requirements of § 135.213
and § 135.225(a).
(d) After completing a landing at the
airport at which a weather report is
not available, the pilot in command is
authorized to determine if the weather
meets the takeoff requirements of part
97 of this chapter or the certificate
holder’s operations specification, as ap-
plicable.
[Doc. No. FAA–2010–0982, 79 FR 9975, Feb. 21,
2014, as amended by Amdt. 135–131, 79 FR
43622, July 28, 2014; Amdt. 135–141, 84 FR
35823, July 25, 2019]
§ 135.613 Approach/departure IFR
transitions.
(a)
Approaches.
When conducting an
authorized instrument approach and
transitioning from IFR to VFR flight,
upon transitioning to VFR flight the
following weather minimums apply—
(1) For Point-in-Space (PinS) Copter
Instrument approaches annotated with
a ‘‘Proceed VFR’’ segment, if the dis-
tance from the missed approach point
to the landing area is 1 NM or less,
flight visibility must be at least 1 stat-
ute mile and the ceiling on the ap-
proach chart applies;
(2) For all instrument approaches, in-
cluding PinS when paragraph (a)(1) of

