
703
Federal Aviation Administration, DOT
§ 91.153
§ 91.147
Passenger carrying flights for
compensation or hire.
Each Operator conducting passenger-
carrying flights for compensation or
hire must meet the following require-
ments unless all flights are conducted
under § 91.146.
(a) For the purposes of this section
and for drug and alcohol testing,
Oper-
ator means any person conducting non-
stop passenger-carrying flights in an
airplane, powered-lift, or rotorcraft for
compensation or hire in accordance
with § 119.1(e)(2), § 135.1(a)(5), or
§ 121.1(d) of this chapter that begin and
end at the same airport and are con-
ducted within a 25-statute mile radius
of that airport.
(b) An Operator must comply with
the safety provisions of part 136, sub-
part A of this chapter, and apply for
and receive a Letter of Authorization
from the responsible Flight Standards
office.
(c) Each application for a Letter of
Authorization must include the fol-
lowing information:
(1) Name of Operator, agent, and any
d/b/a (doing-business-as) under which
that Operator does business;
(2) Principal business address and
mailing address;
(3) Principal place of business (if dif-
ferent from business address);
(4) Name of person responsible for
management of the business;
(5) Name of person responsible for
aircraft maintenance;
(6) Type of aircraft, registration
number(s), and make/model/series; and
(7) An Antidrug and Alcohol Misuse
Prevention Program registration.
(d) The Operator must register and
implement its drug and alcohol testing
programs in accordance with part 120
of this chapter.
(e) The Operator must comply with
the provisions of the Letter of Author-
ization received.
[Doc. No. FAA–1998–4521, 72 FR 6911, Feb. 13,
2007, as amended by Amdt. 91–307, 74 FR
22652, May 14, 2009; Amdt. 91–320, 76 FR 8893,
Feb. 16, 2011; Docket FAA–2018–0119, Amdt.
91–350, 83 FR 9171, Mar. 5, 2018; Docket No.
FAA–2022–1563; Amdt. Nos. 91–370, 88 FR
48087, July 26, 2023]
§§ 91.148–91.149
[Reserved]
V
ISUAL
F
LIGHT
R
ULES
§ 91.151
Fuel requirements for flight in
VFR conditions.
(a) No person may begin a flight in
an airplane under VFR conditions un-
less (considering wind and forecast
weather conditions) there is enough
fuel to fly to the first point of intended
landing and, assuming normal cruising
speed—
(1) During the day, to fly after that
for at least 30 minutes; or
(2) At night, to fly after that for at
least 45 minutes.
(b) No person may begin a flight in a
rotorcraft under VFR conditions unless
(considering wind and forecast weather
conditions) there is enough fuel to fly
to the first point of intended landing
and, assuming normal cruising speed,
to fly after that for at least 20 minutes.
§ 91.153
VFR flight plan: Information
required.
(a)
Information required. Unless other-
wise authorized by ATC, each person
filing a VFR flight plan shall include in
it the following information:
(1) The aircraft identification num-
ber and, if necessary, its radio call
sign.
(2) The type of the aircraft or, in the
case of a formation flight, the type of
each aircraft and the number of air-
craft in the formation.
(3) The full name and address of the
pilot in command or, in the case of a
formation flight, the formation com-
mander.
(4) The point and proposed time of de-
parture.
(5) The proposed route, cruising alti-
tude (or flight level), and true airspeed
at that altitude.
(6) The point of first intended landing
and the estimated elapsed time until
over that point.
(7) The amount of fuel on board (in
hours).
(8) The number of persons in the air-
craft, except where that information is
otherwise readily available to the FAA.
(9) Any other information the pilot in
command or ATC believes is necessary
for ATC purposes.
VerDate Sep<11>2014
14:00 Mar 14, 2024
Jkt 262047
PO 00000
Frm 00713
Fmt 8010
Sfmt 8010
Q:\14\14V2.TXT
PC31
aworley on LAPBH6H6L3 with DISTILLER
704
14 CFR Ch. I (1–1–24 Edition)
§ 91.155
(b)
Cancellation. When a flight plan
has been activated, the pilot in com-
mand, upon canceling or completing
the flight under the flight plan, shall
notify an FAA Flight Service Station
or ATC facility.
§ 91.155
Basic VFR weather minimums.
(a) Except as provided in paragraph
(b) of this section and § 91.157, no per-
son may operate an aircraft under VFR
when the flight visibility is less, or at
a distance from clouds that is less,
than that prescribed for the cor-
responding altitude and class of air-
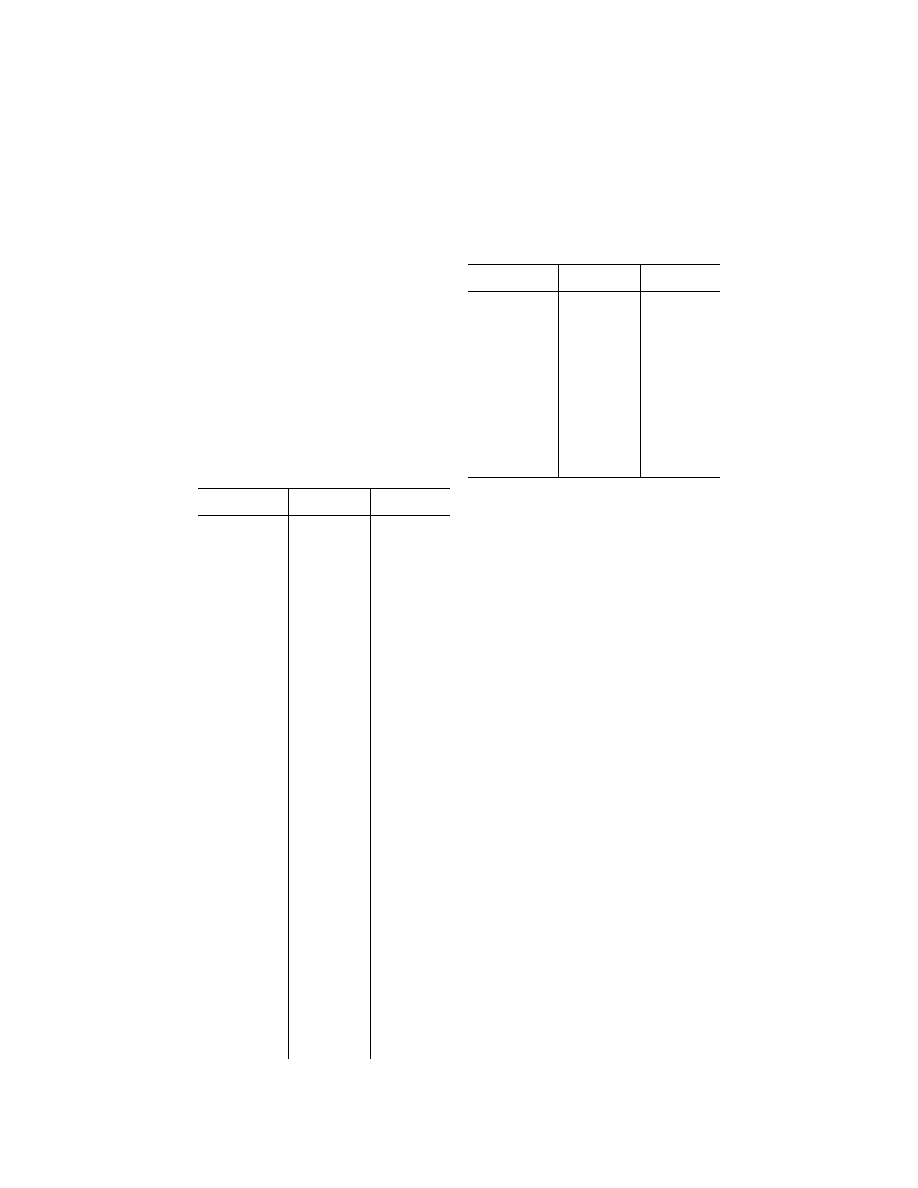
space in the following table:
Airspace Flight
visibility
Distance from
clouds
Class A ....................
Not Applicable ....
Not Applicable.
Class B ....................
3 statute miles ....
Clear of Clouds.
Class C ....................
3 statute miles ....
500 feet below.
.............................
1,000 feet above.
.............................
2,000 feet hori-
zontal.
Class D ....................
3 statute miles ....
500 feet below.
.............................
1,000 feet above.
.............................
2,000 feet hori-
zontal.
Class E:
Less than
10,000 feet
MSL.
3 statute miles ....
500 feet below.
.............................
1,000 feet above.
.............................
2,000 feet hori-
zontal.
At or above
10,000 feet
MSL.
5 statute miles ....
1,000 feet below.
.............................
1,000 feet above.
.............................
1 statute mile hor-
izontal.
Class G:
1,200 feet or
less above
the surface
(regardless of
MSL altitude)
For aircraft other
than helicopters:
Day, except as
provided in
§ 91.155(b).
1 statute mile ......
Clear of clouds.
Night, except as
provided in
§ 91.155(b).
3 statute miles ....
500 feet below.
.............................
1,000 feet above.
.............................
2,000 feet hori-
zontal.
For helicopters:
Day ...................
1
⁄
2
statute mile ....
Clear of clouds
Night, except as
provided in
§ 91.155(b).
1 statute mile ......
Clear of clouds.
More than 1,200
feet above the
surface but
less than
10,000 feet
MSL
Day ............
1 statute mile ......
500 feet below.
Airspace Flight
visibility
Distance from
clouds
.............................
1,000 feet above.
.............................
2,000 feet hori-
zontal.
Night ..........
3 statute miles ....
500 feet below.
.............................
1,000 feet above.
.............................
2,000 feet hori-
zontal.
More than 1,200
feet above the
surface and at
or above
10,000 feet
MSL.
5 statute miles ....
1,000 feet below.
.............................
1,000 feet above.
.............................
1 statute mile hor-
izontal.
(b)
Class G Airspace. Notwithstanding
the provisions of paragraph (a) of this
section, the following operations may
be conducted in Class G airspace below
1,200 feet above the surface:
(1)
Helicopter. A helicopter may be op-
erated clear of clouds in an airport
traffic pattern within
1
⁄
2
mile of the
runway or helipad of intended landing
if the flight visibility is not less than
1
⁄
2
statute mile.
(2)
Airplane, powered parachute, or
weight-shift-control aircraft. If the visi-
bility is less than 3 statute miles but
not less than 1 statute mile during
night hours and you are operating in
an airport traffic pattern within
1
⁄
2
mile of the runway, you may operate
an airplane, powered parachute, or
weight-shift-control aircraft clear of
clouds.
(c) Except as provided in § 91.157, no
person may operate an aircraft beneath
the ceiling under VFR within the lat-
eral boundaries of controlled airspace
designated to the surface for an airport
when the ceiling is less than 1,000 feet.
(d) Except as provided in § 91.157 of
this part, no person may take off or
land an aircraft, or enter the traffic
pattern of an airport, under VFR, with-
in the lateral boundaries of the surface
areas of Class B, Class C, Class D, or
Class E airspace designated for an air-
port—
(1) Unless ground visibility at that
airport is at least 3 statute miles; or
(2) If ground visibility is not reported
at that airport, unless flight visibility
during landing or takeoff, or while op-
erating in the traffic pattern is at least
3 statute miles.
VerDate Sep<11>2014
14:00 Mar 14, 2024
Jkt 262047
PO 00000
Frm 00714
Fmt 8010
Sfmt 8010
Q:\14\14V2.TXT
PC31
aworley on LAPBH6H6L3 with DISTILLER

