
823
Federal Aviation Administration, DOT
§ 91.1705
command, or other persons who manip-
ulate the controls while under the su-
pervision of a pilot in command.
(c) This subpart also applies to those
persons who provide pilot training for a
Mitsubishi MU–2B series airplane. The
requirements in this subpart are in ad-
dition to the requirements of parts 61,
91, and 135 of this chapter.
§ 91.1703
Compliance and eligibility.
(a) Except as provided in paragraph
(b) of this section, no person may ma-
nipulate the controls, act as PIC, act
as second-in-command, or provide pilot
training for a Mitsubishi MU–2B series
airplane unless that person meets the
requirements of this subpart.
(b) A person who does not meet the
requirements of this subpart may ma-
nipulate the controls of a Mitsubishi
MU–2B series airplane if a pilot in com-
mand who meets the requirements of
this subpart is occupying a pilot sta-
tion, no passengers or cargo are carried
on board the airplane, and the flight is
being conducted for one of the fol-
lowing reasons—
(1) The pilot in command is providing
pilot training to the manipulator of
the controls;
(2) The pilot in command is con-
ducting a maintenance test flight with
a second pilot or certificated mechanic;
or
(3) The pilot in command is con-
ducting simulated instrument flight
and is using a safety pilot other than
the pilot in command who manipulates
the controls for the purposes of
§ 91.109(b).
(c) A person is required to complete
Initial/transition training if that person
has fewer than—
(1) 50 hours of documented flight
time manipulating the controls while
serving as pilot in command of a
Mitsubishi MU–2B series airplane in
the preceding 24 months; or
(2) 500 hours of documented flight
time manipulating the controls while
serving as pilot in command of a
Mitsubishi MU–2B series airplane.
(d) A person is eligible to receive
Re-
qualification training in lieu of Initial/
transition training if that person has
at least—
(1) 50 hours of documented flight
time manipulating the controls while
serving as pilot in command of a
Mitsubishi MU–2B series airplane in
the preceding 24 months; or
(2) 500 hours of documented flight
time manipulating the controls while
serving as pilot in command of a
Mitsubishi MU–2B series airplane.
(e) A person is required to complete
Recurrent training within the preceding
12 months. Successful completion of
Initial/transition or Requalification
training within the preceding 12
months satisfies the requirement of
Recurrent training. A person must suc-
cessfully complete Initial/transition
training or Requalification training be-
fore being eligible to receive Recurrent
training.
(f) Successful completion of Initial/
transition training or Requalification
training is a one-time requirement. A
person may elect to retake Initial/tran-
sition training or Requalification
training in lieu of Recurrent training.
(g) A person is required to complete
Differences training in accordance with
an FAA approved MU–2B training pro-
gram if that person operates more than
one MU–2B model as specified in
§ 91.1707(c).
§ 91.1705
Required pilot training.
(a) Except as provided in § 91.1703(b),
no person may manipulate the con-
trols, act as pilot in command, or act
as second-in-command of a Mitsubishi
MU–2B series airplane for the purpose
of flight unless—
(1) The requirements for ground and
flight training on Initial/transition,
Requalification, Recurrent, and Dif-
ferences training have been completed
in accordance with an FAA approved
MU–2B training program that meets
the standards of this subpart; and
(2) That person’s logbook has been
endorsed in accordance with paragraph
(f) of this section.
(b) Except as provided in § 91.1703(b),
no person may manipulate the con-
trols, act as pilot in command, or act
as second-in-command, of a Mitsubishi
MU–2B series airplane for the purpose
of flight unless—
(1) That person satisfactorily com-
pletes, if applicable, annual Recurrent
pilot training on the
Special Emphasis
VerDate Sep<11>2014
14:00 Mar 14, 2024
Jkt 262047
PO 00000
Frm 00833
Fmt 8010
Sfmt 8010
Q:\14\14V2.TXT
PC31
aworley on LAPBH6H6L3 with DISTILLER

824
14 CFR Ch. I (1–1–24 Edition)
§ 91.1705
Items, and all items listed in the Train-
ing Course Final Phase Check in accord-
ance with an FAA approved MU–2B
training program that meets the stand-
ards of this subpart; and
(2) That person’s logbook has been
endorsed in accordance with paragraph
(f) of this section.
(c) Satisfactory completion of the
competency check required by § 135.293
of this chapter within the preceding 12
calendar months may not be sub-
stituted for the Mitsubishi MU–2B se-
ries airplane annual recurrent flight
training of this section.
(d) Satisfactory completion of a Fed-
eral Aviation Administration spon-
sored pilot proficiency program, as de-
scribed in § 61.56(e) of this chapter may
not be substituted for the Mitsubishi
MU–2B series airplane annual recurrent
flight training of this section.
(e) If a person complies with the re-
quirements of paragraph (a) or (b) of
this section in the calendar month be-
fore or the calendar month after the
month in which compliance with these
paragraphs are required, that person is
considered to have accomplished the
training requirement in the month the
training is due.
(f) The endorsement required under
paragraph (a) and (b) of this section
must be made by—
(1) A certificated flight instructor or
a simulator instructor authorized by a
Training Center certificated under part
142 of this chapter and meeting the
qualifications of § 91.1713; or
(2) For persons operating the
Mitsubishi MU–2B series airplane for a
14 CFR part 119 certificate holder with-
in the last 12 calendar months, the part
119 certificate holder’s flight instructor
if authorized by the FAA and if that
flight instructor meets the require-
ments of § 91.1713.
(g) All training conducted for a
Mitsubishi MU–2B series airplane must
be completed in accordance with an
MU–2B series airplane checklist that
has been accepted by the Federal Avia-
tion Administration’s MU–2B Flight
Standardization Board or the applica-
ble MU–2B series checklist (incor-
porated by reference, see § 91.1721).
(h) MU–2B training programs must
contain ground training and flight
training sufficient to ensure pilot pro-
ficiency for the safe operation of MU–
2B aircraft, including:
(1) A ground training curriculum suf-
ficient to ensure pilot knowledge of
MU–2B aircraft, aircraft systems, and
procedures, necessary for safe oper-
ation; and
(2) Flight training curriculum includ-
ing flight training maneuver profiles
sufficient in number and detail to en-
sure pilot proficiency in all MU–2B op-
erations for each MU–2B model in cor-
relation with MU–2B limitations, pro-
cedures, aircraft performance, and MU–
2B Cockpit Checklist procedures appli-
cable to the MU–2B model being
trained. A MU–2B training program
must contain, at a minimum, the fol-
lowing flight training maneuver pro-
files applicable to the MU–2B model
being trained:
(i) Normal takeoff with 5- and 20- de-
grees flaps;
(ii) Takeoff engine failure with 5- and
20- degrees flaps;
(iii) Takeoff engine failure on runway
or rejected takeoff;
(iv) Takeoff engine failure after lift-
off—unable to climb (may be completed
in classroom or flight training device
only);
(v) Steep turns;
(vi) Slow flight maneuvers;
(vii) One engine inoperative maneu-
vering with loss of directional control;
(viii) Approach to stall in clean con-
figuration and with wings level;
(ix) Approach to stall in takeoff con-
figuration with 15- to 30- degrees bank;
(x) Approach to stall in landing con-
figuration with gear down and 40-de-
grees of flaps;
(xi) Accelerated stall with no flaps;
(xii) Emergency descent at low speed;
(xiii) Emergency descent at high
speed;
(xiv) Unusual attitude recovery with
the nose high;
(xv) Unusual attitude recovery with
the nose low;
(xvi) Normal landing with 20- and 40-
degrees flaps;
(xvii) Go around and rejected land-
ing;
(xviii) No flap or 5- degrees flaps
landing;
(xix) One engine inoperative landing
with 5- and 20- degrees flaps;
(xx) Crosswind landing;
VerDate Sep<11>2014
14:00 Mar 14, 2024
Jkt 262047
PO 00000
Frm 00834
Fmt 8010
Sfmt 8010
Q:\14\14V2.TXT
PC31
aworley on LAPBH6H6L3 with DISTILLER
825
Federal Aviation Administration, DOT
§ 91.1707
(xxi) Instrument landing system
(ILS) and missed approach ;
(xxii) Two engine missed approach;
(xxiii) One engine inoperative ILS
and missed approach;
(xxiv) One engine inoperative missed
approach;
(xxv) Non-precision and missed ap-
proach;
(xxvi) Non-precision continuous de-
scent final approach and missed ap-
proach;
(xxvii) One engine inoperative non-
precision and missed approach;
(xxviii) One engine inoperative non-
precision CDFA and missed approach;
(xxix) Circling approach at weather
minimums;
(xxx) One engine inoperative circling
approach at weather minimums.
(3) Flight training must include a
final phase check sufficient to docu-
ment pilot proficiency in the flight
training maneuver profiles at the com-
pletion of training; and
(4) Differences training for applicable
MU–2B model variants sufficient to en-
sure pilot proficiency in each model op-
erated. Current MU–2B differences re-
quirements are specified in § 91.1707(c).
A person must complete Differences
training if a person operates more than
one MU–2B model as specified in
§ 91.1707(c). Differences training be-
tween the factory type design K and M
models of the MU–2B airplane, and the
factory type design J and L models of
the MU–2B airplane, may be accom-
plished with Level A training. All
other factory type design differences
training must be accomplished with
Level B training unless otherwise spec-
ified in § 91.1707(c) . A Level A or B dif-
ferences training is not a recurring an-
nual requirement. Once a person has
completed Initial Level A or B Dif-
ferences training between the applica-
ble different models, no additional dif-
ferences training between those models
is required.
(5) Icing training sufficient to ensure
pilot knowledge and safe operation of
the MU–2B aircraft in icing conditions
as established by the FAA;
(6) Ground and flight training pro-
grams must include training hours
identified by § 91.1707(a) for ground in-
struction, § 91.1707(b) for flight instruc-
tion, and § 91.1707(c) for differences
training.
(i) No training credit is given for sec-
ond-in-command training and no credit
is given for right seat time under this
program. Only the sole manipulator of
the controls of the MU–2B airplane,
flight training device, or Level C or D
simulator can receive training credit
under this program;
(ii) An MU–2B airplane must be oper-
ated in accordance with an FAA ap-
proved MU–2B training program that
meets the standards of this subpart and
the training hours in § 91.1707.
(7) Endorsements given for compli-
ance with paragraph (f) of this section
must be appropriate to the content of
that specific MU–2B training program’s
compliance with standards of this sub-
part.
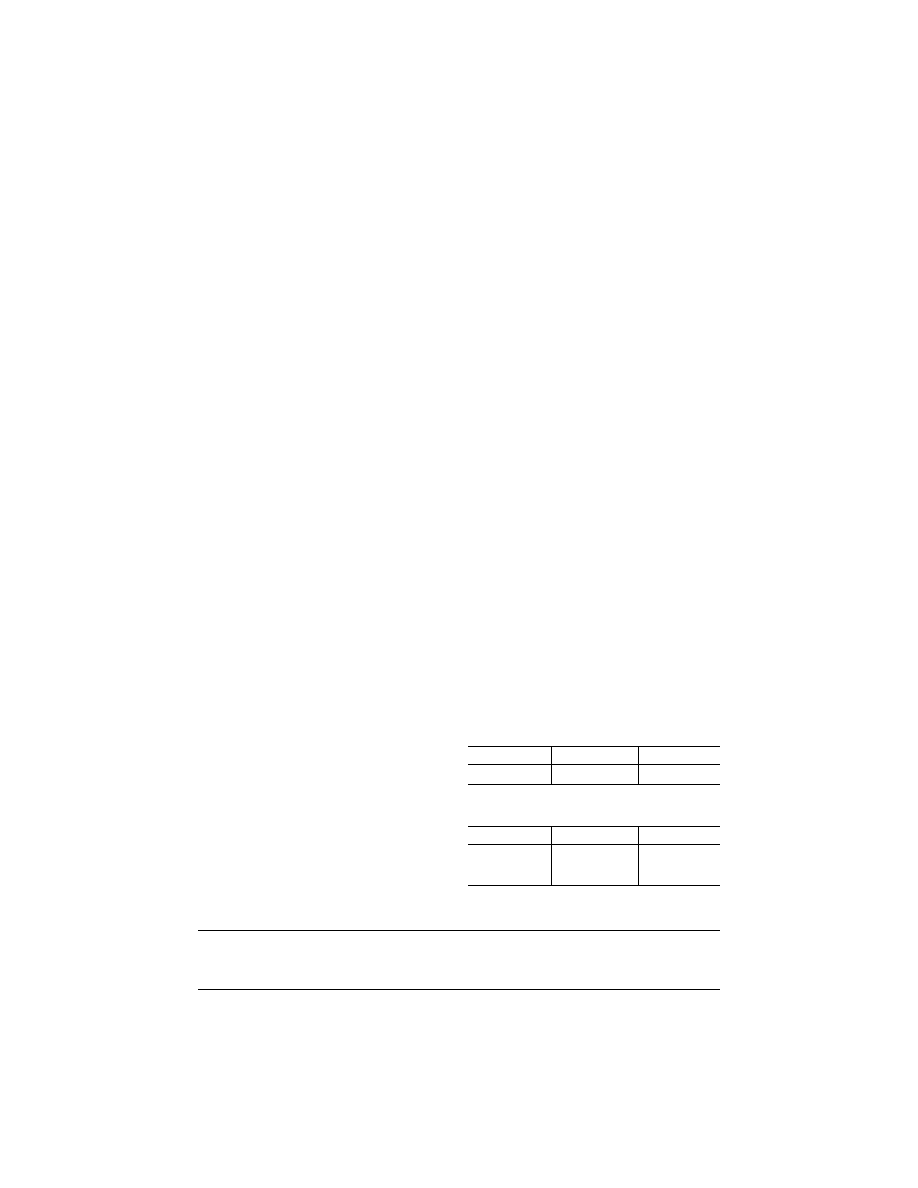
§ 91.1707
Training program hours.
(a) Ground instruction hours are list-
ed in the following table:
Initial/transition Requalification
Recurrent
20 hours ...............
12 hours ...............
8 hours.
(b) Flight instruction hours are listed
in the following table:
Initial/transition Requalification
Recurrent
12 hours with a
minimum of 6
hours at level E.
8 hours level C or
level E.
4 hours at level E,
or 6 hours at
level C.
(c) Differences training hours are
listed in the following table:
2 factory type design models concurrently ......................
1.5 hours required at level B.
More than 2 factory type design models concurrently ....
3 hours at level B.
Each additional factory type design model added sepa-
rately.
1.5 hours at level B.
(d) Definitions of levels of training as
used in this subpart:
(1) LEVEL A Training—Training that
is conducted through self-instruction
by the pilot.
VerDate Sep<11>2014
14:00 Mar 14, 2024
Jkt 262047
PO 00000
Frm 00835
Fmt 8010
Sfmt 8010
Q:\14\14V2.TXT
PC31
aworley on LAPBH6H6L3 with DISTILLER


