AIM
4/20/23
g. Night LZs
1.
There are several ways to light a night LZ:
(a)
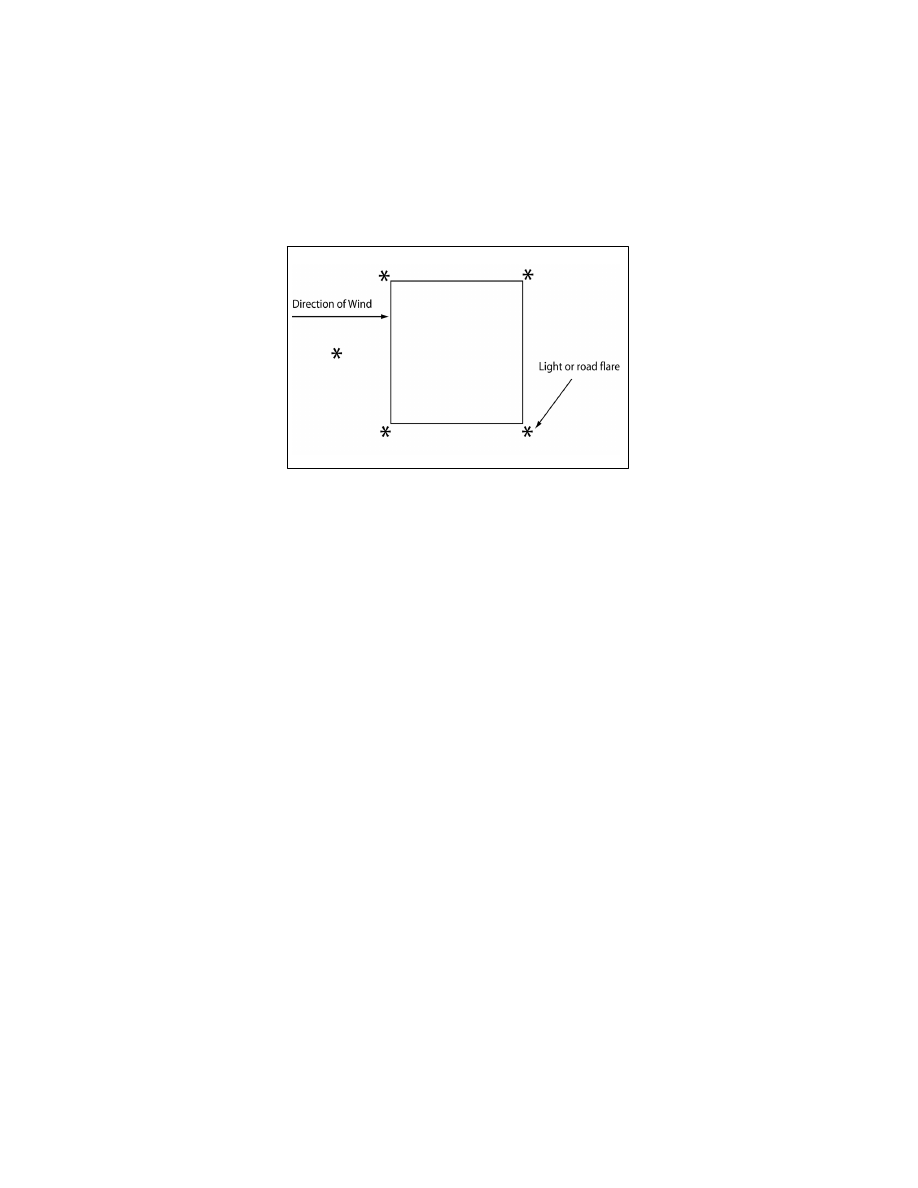
Mark the touchdown area with five lights or road flares, one in each corner and one indicating the
direction of the wind. See FIG 10
FIG 10
−
2
−
7
Recommended Lighting for Landing Zone Operations at Night
NOTE
−
Road flares are an intense source of ignition and may be unsuitable or dangerous in certain conditions. In any case, they
must be closely managed and firefighting equipment should be present when used. Other light sources are preferred, if
available.
(b)
If chemical light sticks may be used, care should be taken to assure they are adequately secured against
being dislodged by the helicopter’s rotor wash.
(c)
Another method of marking a LZ uses four emergency vehicles with their low beam headlights aimed
toward the intended landing area.
(d)
A third method for marking a LZ uses two vehicles. Have the vehicles direct their headlight beams
into the wind, crossing at the center of the LZ. (If fire/rescue personnel are available, the reflective stripes on
their bunker gear will assist the pilot greatly.)
2.
At night, spotlights, flood lights and hand lights used to define the LZ are not to be pointed at the
helicopter. However, they are helpful when pointed toward utility poles, trees or other hazards to the landing
aircraft. White lights such as spotlights, flashbulbs and hi
−
beam headlights ruin the pilot’s night vision and
temporarily blind him. Red lights, however, are very helpful in finding accident locations and do not affect the
pilot’s night vision as significantly.
3.
As in Day LZ operations, ensure radio contact is accomplished between ground and air, if possible.
h. Ground Guide
1.
When the helicopter is in sight, one person should assist the LZ Coordinator by guiding the helicopter
into a safe landing area. In selecting an LZ Coordinator, recognize that medical personnel usually are very busy
with the patient at this time. It is recommended that the LZ Coordinator be someone other than a medical
responder, if possible. Eye protection should be worn. The ground guide should stand with his/her back to the
wind and his/her arms raised over his/her head (flashlights in each hand for night operations.)
2.
The pilot will confirm the LZ sighting by radio. If possible, once the pilot has identified the LZ, the
ground guide should move out of the LZ.
3.
As the helicopter turns into the wind and begins a descent, the LZ coordinator should provide assistance
by means of radio contact, or utilize the “unsafe signal” to wave off the helicopter if the LZ is not safe (see
8). The LZ Coordinator should be far enough from the touchdown area that he/she can still maintain
visual contact with the pilot.
10
−
2
−
16
Special Operations